In today’s fast-paced and competitive world of technology, businesses are constantly seeking innovative ways to captivate and retain their customers. In the digital realm, user experience has emerged as a critical factor for success. While functionality and usability remain essential, emotional design has taken center stage in creating user-centric experiences that leave a lasting impact on users. This approach recognizes that emotions play a significant role in decision-making and brand loyalty, and understanding the psychology behind it can lead to remarkable results.
The Connection Between Emotions and Design:
At its core, emotional design is about understanding human emotions and incorporating that understanding into the design process. Emotions are powerful drivers of behavior, influencing our decisions, memories, and overall satisfaction. As users interact with a product or service, they form emotional connections that shape their perceptions and attitudes towards it. By tapping into these emotional responses, designers can create experiences that resonate deeply with users.
Emotional design extends beyond just aesthetics; it encompasses the overall experience, from the visual elements to the tone of communication and the functionality of the product. Consider a website or app that provides a seamless and intuitive experience with vibrant visuals and friendly messaging. Such a design fosters positive emotions and makes users feel valued and engaged. On the other hand, a confusing or frustrating interface can evoke negative emotions, leading to user frustration and abandonment.
Three Levels of Emotional Design:
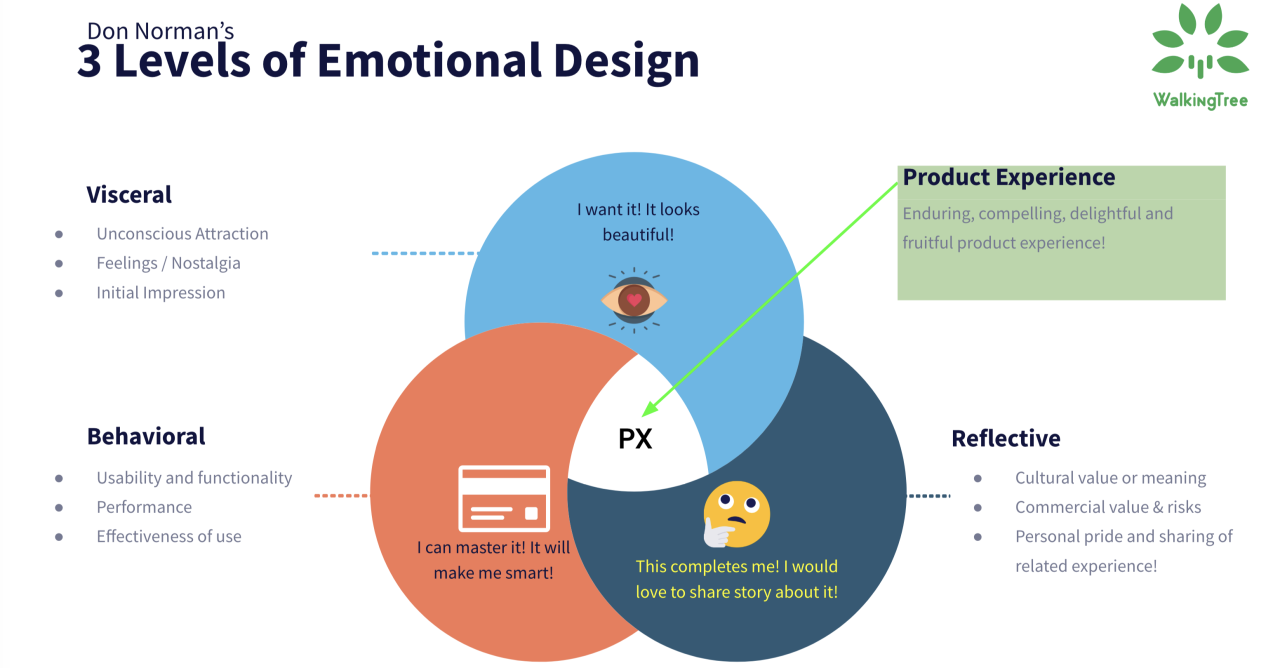
Don Norman, a renowned cognitive scientist and usability expert, introduced the concept of emotional design and categorized it into three levels: visceral, behavioral, and reflective.
- Visceral Level: At the visceral level, design elicits immediate and instinctive emotional reactions. This level deals with the initial impact of a product’s appearance. Colors, shapes, textures, and other sensory aspects contribute to these emotional responses. For example, a sleek and modern smartphone design can evoke a sense of desire and luxury.
- Behavioral Level: The behavioral level focuses on the pleasure and effectiveness derived from using a product. It involves how well a product performs its intended function and how user-friendly it is. A well-designed product that meets users’ needs and expectations can create feelings of joy and satisfaction. Conversely, a product that is difficult to use or fails to deliver on its promises can lead to frustration and disappointment.
- Reflective Level: The reflective level deals with the meaning and symbolism a product holds for its users. It encompasses the emotional connection and memories associated with the product. Products that align with a user’s self-image or values can evoke feelings of pride and loyalty. For example, a brand that promotes eco-friendly values can create a sense of pride and identity for environmentally conscious customers.
The Role of Empathy in Emotional Design:
Empathy is a fundamental aspect of emotional design. Designers must put themselves in the shoes of the users, understanding their needs, desires, and pain points. By empathizing with the target audience, designers can craft experiences that resonate with users on a deeper level.
User research, such as interviews, surveys, and usability testing, is a valuable tool in understanding user emotions. It helps uncover the users’ motivations, preferences, and emotional responses to various design elements. Armed with this knowledge, designers can make informed decisions that align with the users’ emotional expectations.
Storytelling and Emotional Engagement:
Storytelling is a powerful technique used in emotional design to create meaningful connections with users. Human beings are naturally drawn to narratives, and a well-told story can elicit a wide range of emotions. Brands often use storytelling to convey their values, mission, and personality, thereby forging emotional connections with their audience.
By incorporating storytelling elements into their design, such as relatable characters, scenarios, and journeys, designers can evoke emotions that resonate with users’ personal experiences. This emotional engagement leaves a lasting impression, enhancing brand recall and loyalty.
The Impact of Emotional Design on Brand Loyalty:
Emotional design goes beyond creating a one-time positive experience. It aims to foster long-term relationships and brand loyalty. When users develop positive emotional associations with a product or brand, they are more likely to become repeat customers and brand advocates.
Loyal customers are not just satisfied with a product; they are emotionally invested in it. They become a part of the brand’s community and actively promote it through word-of-mouth marketing. Building such emotional loyalty requires a consistent and thoughtful design that consistently meets and exceeds user expectations.
Avoiding Manipulation and Ethical Considerations:
While emotional design can be a powerful tool for creating positive experiences, there is a fine line between eliciting genuine emotions and manipulating users. Designers must be mindful of ethical considerations and avoid exploiting users’ emotions for financial gain.
Transparency and honesty are essential in the design process. Communicating the purpose and functionality of a product ensures that users are making informed decisions based on their actual needs rather than succumbing to emotional manipulation.
Emotional design is a multidimensional approach that takes into account the psychological and emotional aspects of user experiences. By understanding the three levels of emotional design and embracing empathy and storytelling, designers can create user-centric experiences that resonate deeply with users. Brands that prioritize emotional design can foster loyal customer relationships, leading to long-term success and differentiation in today’s competitive market. However, designers must approach emotional design ethically and responsibly, ensuring that users’ emotions are respected and valued throughout the design journey.
For more blogs related to communication design: https://www.dotsod.in/category/communication-design/
Follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/dotschoolofdesign/