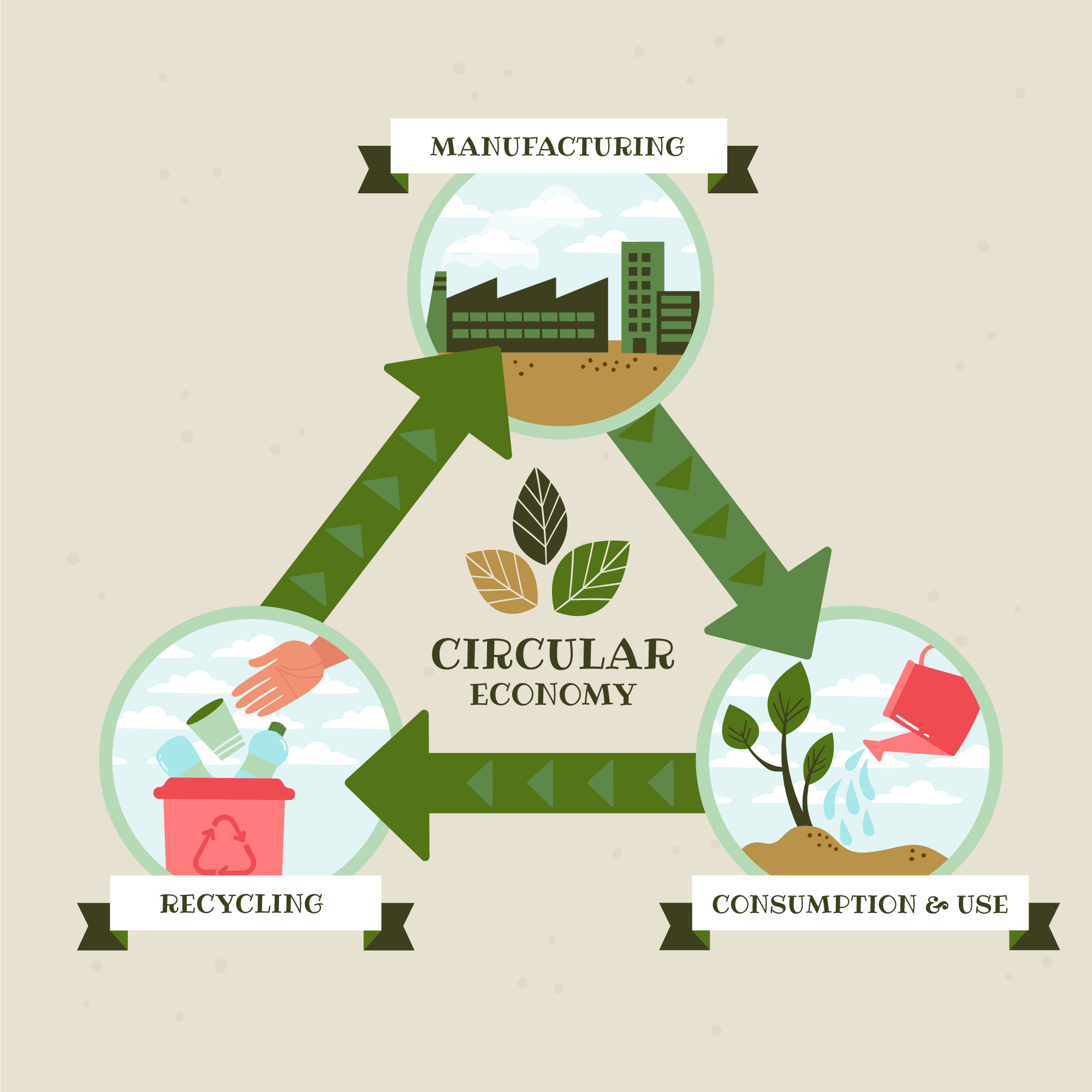
In the contemporary era, where environmental concerns are at the forefront of global discussions, the concept of “Design for Recycling” has emerged as a pivotal element in industrial design. As we grapple with the consequences of excessive waste and limited resources, designers are now called upon to integrate sustainability into their creative processes. This paradigm shift towards eco-friendly design not only contributes to environmental conservation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for products that prioritize recyclability.
The Principles of Design for Recycling in Industrial Design
Design for Recycling is an approach that encourages designers to consider the entire lifecycle of a product, with a particular emphasis on its end-of-life stage. By incorporating recyclability into the design process, industrial designers can minimize the environmental impact of their creations. Here are some key principles that guide Design for Recycling:
- Material Selection: One of the fundamental aspects of designing for recycling is the careful consideration of materials. Opting for easily recyclable materials and minimizing the use of composite or mixed materials makes the recycling process more efficient.
- Simplified Assembly: Complex assembly processes often hinder the recycling of products. Designing products with fewer components and connections not only reduces manufacturing costs but also facilitates disassembly for recycling purposes.
- Marking for Identification: Clear and standardized marking of materials used in a product enables easy identification during the recycling process. This ensures that materials are sorted correctly, streamlining the recycling chain.
- Modularity and Standardization: Designing products with modular components and adhering to standardized sizes makes it easier to replace or upgrade specific parts. This modularity promotes a circular economy by extending the lifespan of products and reducing overall waste.
Challenges in Implementing Design for Recycling
While the principles of Design for Recycling are sound in theory, their implementation comes with challenges that designers must navigate. Some of these challenges include:
- Balancing Aesthetics with Sustainability: Striking a balance between creating visually appealing products and adhering to sustainable principles can be challenging. Designers often face the dilemma of sacrificing aesthetics for recyclability.
- Cost Considerations: Integrating recyclability into the design process may incur additional costs, especially if using alternative materials or implementing complex recycling-friendly features. Balancing these costs without compromising the economic viability of the product is a constant challenge.
- Consumer Awareness: For Design for Recycling to be effective, consumers need to be aware of the recyclability of products and make environmentally conscious choices. Educating consumers on the importance of recycling and the impact of their choices is a significant hurdle.
The Potential of Design for Recycling in Industrial Design
Despite the challenges, the potential benefits of incorporating Design for Recycling into industrial design are substantial:
- Resource Conservation: Design for Recycling contributes to the efficient use of resources by ensuring that materials can be recovered and reused. This approach aligns with the principles of a circular economy, where resources are kept in use for as long as possible.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Products designed for recycling have a lower environmental impact as they minimize the need for raw material extraction and reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills. This, in turn, helps in mitigating climate change and conserving natural ecosystems.
- Brand Reputation and Consumer Loyalty: With an increasing emphasis on sustainability, consumers are becoming more discerning about the environmental impact of the products they purchase. Designing products with recyclability in mind enhances a brand’s reputation and fosters consumer loyalty.
In the evolving landscape of industrial design, the adoption of Design for Recycling is not just a trend but a necessity. As the global community grapples with the challenges of climate change and resource depletion, designers play a pivotal role in shaping a more sustainable future. By embracing the principles of Design for Recycling, industrial designers can contribute to the creation of products that not only meet the functional and aesthetic needs of consumers but also uphold the principles of environmental responsibility. The integration of sustainable practices in industrial design is not just a choice; it is an imperative step towards a harmonious coexistence with our planet.
For more blogs related to design: https://www.dotsod.in/blog/
Follow DOT School of Design on Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Medium and YouTube